Above the fold: a visual history of the internet
Take your browsing low-fi with Taschen’s fascinating – and very physical volume – on the history of web design
Regarded as the ‘biggest thing to happen since the industrial revolution’, the web has changed the world. Here, we look to Taschen’s Web Design: The evolution of the digital world 1990 – today to celebrate the moments, sites and people who have made the biggest impact in its 30-year history.
Written by Rob Ford, web designer and founder of the FWA (Favourite Website Awards), the book is based on Ford’s extensive experience being at the epicentre of the web design revolution, observing its progression, new trends and technology since the 1990s – many of which we take for granted today.
From covering the creation of pioneering design sites such as MONO*crafts and Periscope, to the first website to use surround sound – Ford highlights the World Wide Web’s ability to provide a space for unlimited creative experimentation.
Each chapter features fascinating facts of the year that visualise the immense growth of the web – in 1998 Google and iMac had only just launched and 3.6 per cent of the world population used the internet – fast forward ten years to 2008, and 23.6 per cent of the world population uses the internet, Google is the website with the most traffic globally and Apple launches it’s App Store.
In fact, the web is progressing at such speed we are already in a new digital era – the introduction of AI and smartphones have subsequently made the majority of previous design software redundant.
The most notable rise and fall was Flash software. Launched in 1997, Macromedia Flash changed the online world – which Ford outlines in the first chapter. Flash was and still is responsible for some of the web’s most ambitious and innovative design work.

Other key advances include
2Advanced Studios v3 Expansions – launched in 2001 by the seminal developer Eric Jordan, the website is regarded as the most influential Flash design of all time.
Eye4U – The website’s bright colours and uplifting music made the 1998 page an instant global phenomenon.
Praystation – Another 1998 masterpiece, Praystation was developed by the huge web personality, Joshua Davis. Davis’s Praystation was a pioneer in web art and open-soured code.
Tokyoplastic – Upon its release in 2003 Tokyoplastic gained instant fame and stardom for its exciting flash animation design – quickly scoring huge clients such as MTV. Tokyoplastic still exists today, predominately focusing on animation art and film.

Tokyoplastic
Inevitably all good things come to an end – 2007 saw the introduction of the first iPhone and signaled the downfall of Macromedia Flash. Steve Jobs associated the use of Flash with a bygone era of PCs, neither the iPhone or iPad supported Flash and by 2010 it was dead.
From the ashes of Macromedia Flash emerged a new Internet era: HTML5. Driven by user-friendly interface app experiences, the arrival of HTML5 was hailed as the future of mobile devices and kick-started a new pace in technological advances – but as Ford points out, signified web-design’s move away from the creativity that Flash enabled.

By 2016 Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Reality had come to the web, already a different world to when HTML5 was first introduced five years ago – 49.5 per cent of the global population now used the Internet and there were one billion active websites.
Web Design: The evolution of the digital world 1990 – today reflects on this by spotlighting how user habits have changed, people have shifted to mobile phones from desktops – web-design is evolving to merge real life with digital and through the power of social media, demand for needs-driven templates overtook long-stay experimental apps.

For example, the launch of iPhone X in 2018 introduced Stinkmoji – a facial-recognition web experience celebrating iconic pop-culture characters designed as an ode to Apple’s Animoji. Users could use their camera to bring the characters to life with facial expressions and then upload their personalised videos to social media platforms such as YouTube and Instagram.
Ford summarises his 30-year observation by looking to our digital future and raising questions over what does web-design mean entering in a new decade. The market is now pointed towards apps that provide information in quick and recognisable formats – this has led designers taking extreme directions to achieve the best new innovations. So, what’s next for web-design?

Stinkmoji
INFORMATION
Wallpaper* Newsletter
Receive our daily digest of inspiration, escapism and design stories from around the world direct to your inbox.
-
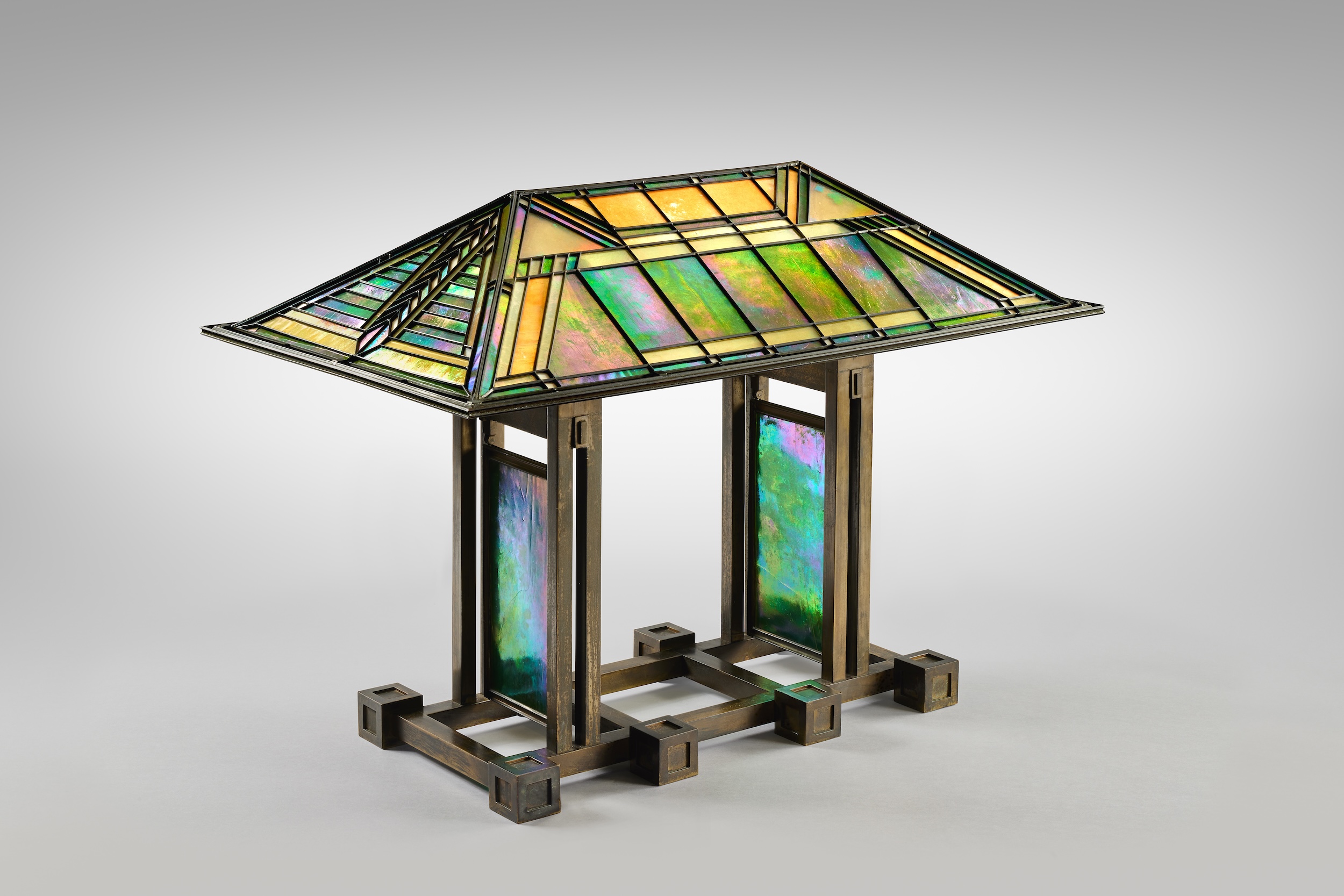 Sotheby’s is auctioning a rare Frank Lloyd Wright lamp – and it could fetch $5 million
Sotheby’s is auctioning a rare Frank Lloyd Wright lamp – and it could fetch $5 millionThe architect's ‘Double-Pedestal’ lamp, which was designed for the Dana House in 1903, is hitting the auction block 13 May at Sotheby's.
By Anna Solomon
-
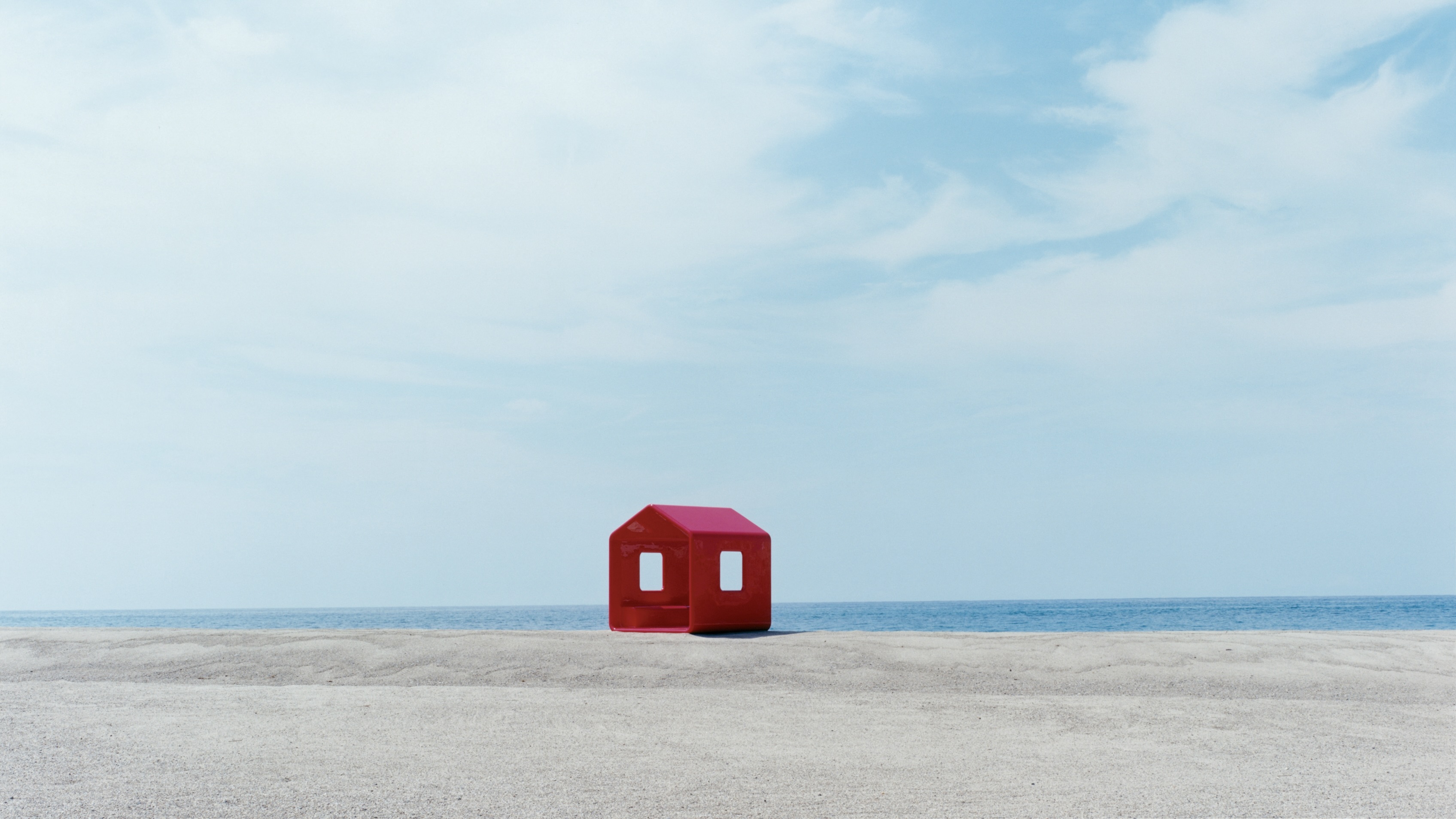 Naoto Fukasawa sparks children’s imaginations with play sculptures
Naoto Fukasawa sparks children’s imaginations with play sculpturesThe Japanese designer creates an intuitive series of bold play sculptures, designed to spark children’s desire to play without thinking
By Danielle Demetriou
-
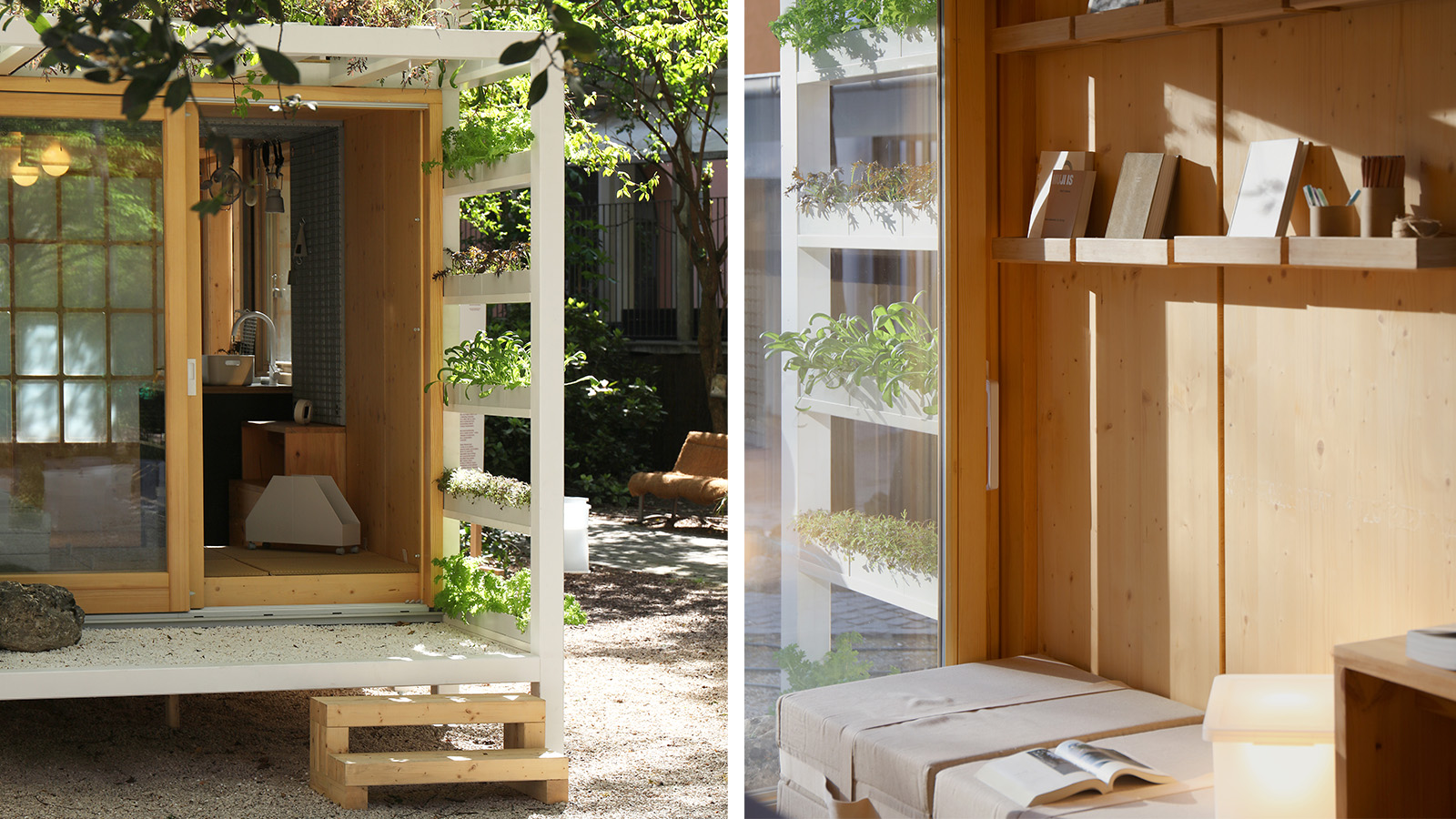 Japan in Milan! See the highlights of Japanese design at Milan Design Week 2025
Japan in Milan! See the highlights of Japanese design at Milan Design Week 2025At Milan Design Week 2025 Japanese craftsmanship was a front runner with an array of projects in the spotlight. Here are some of our highlights
By Danielle Demetriou
-
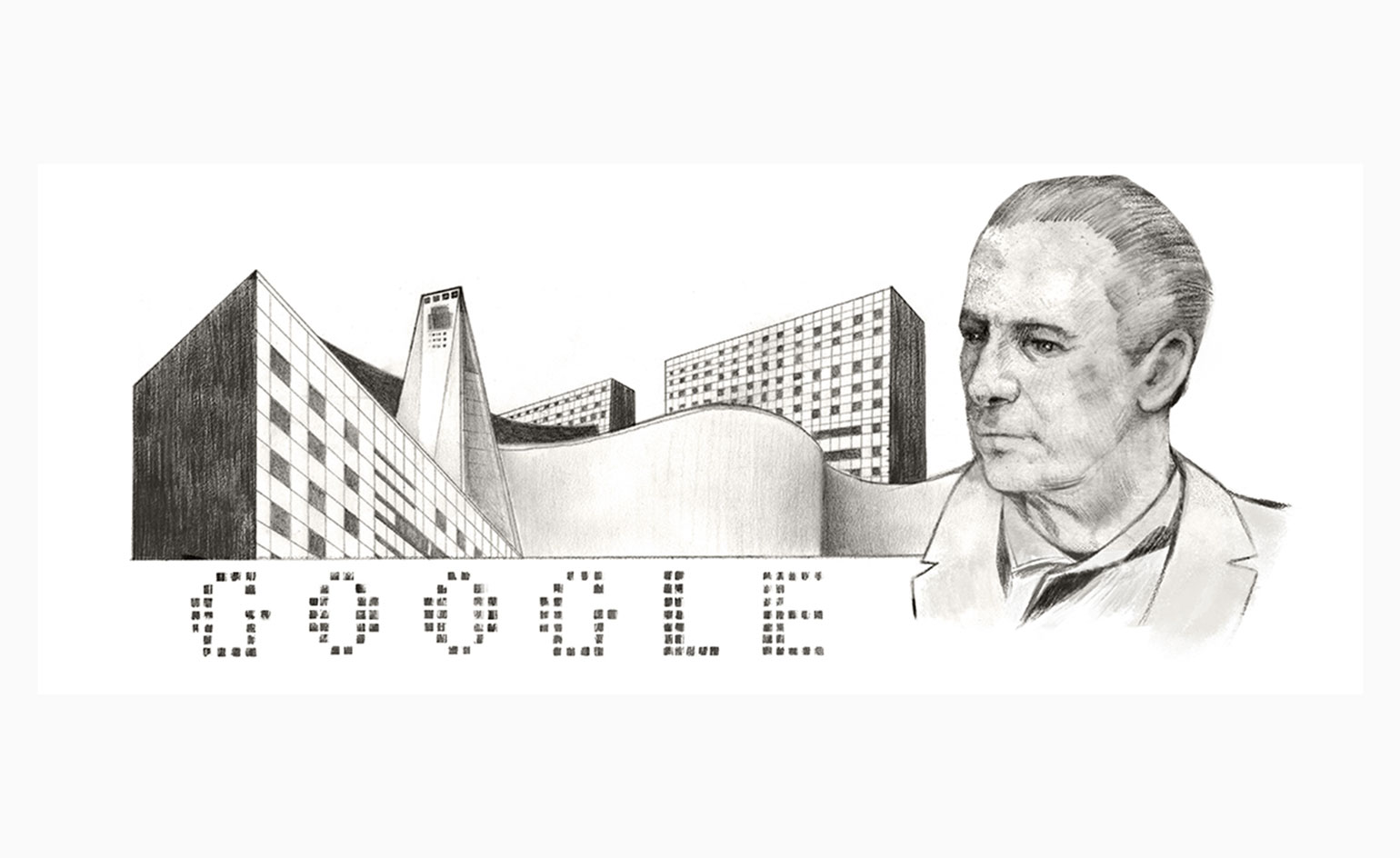 The finest Google Doodles of all time
The finest Google Doodles of all timeOn 20 August 1998, a week before a two-year-old Google become an incorporated company, founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin were heading to Burning Man festival. To mark themselves ‘out of office’ on their email signatures, they decided to overlay the famous Burning Man stick-figure on the Google logo (which then came with a Yahoo-style exclamation mark, as if it needed to announce itself). The idea lay dormant until 2010, when then-intern Dennis Hwang (who went onto become Google webmaster, amongst other more recent titles) was tasked with decorating the logo for Bastille Day, sparking eight years of marking important moments in history with a graphic, digital ephitaph. What started as an ‘out of office’ scribble has become an artform, celebrating Calder to Kadinsky; Zaha Hadid to Mies van der Rohe.
By Elly Parsons
-
 Nike plots the London Fuel Map
Nike plots the London Fuel MapBy Nick Compton